Distributed Processing Basics
What is Distributed Processing?
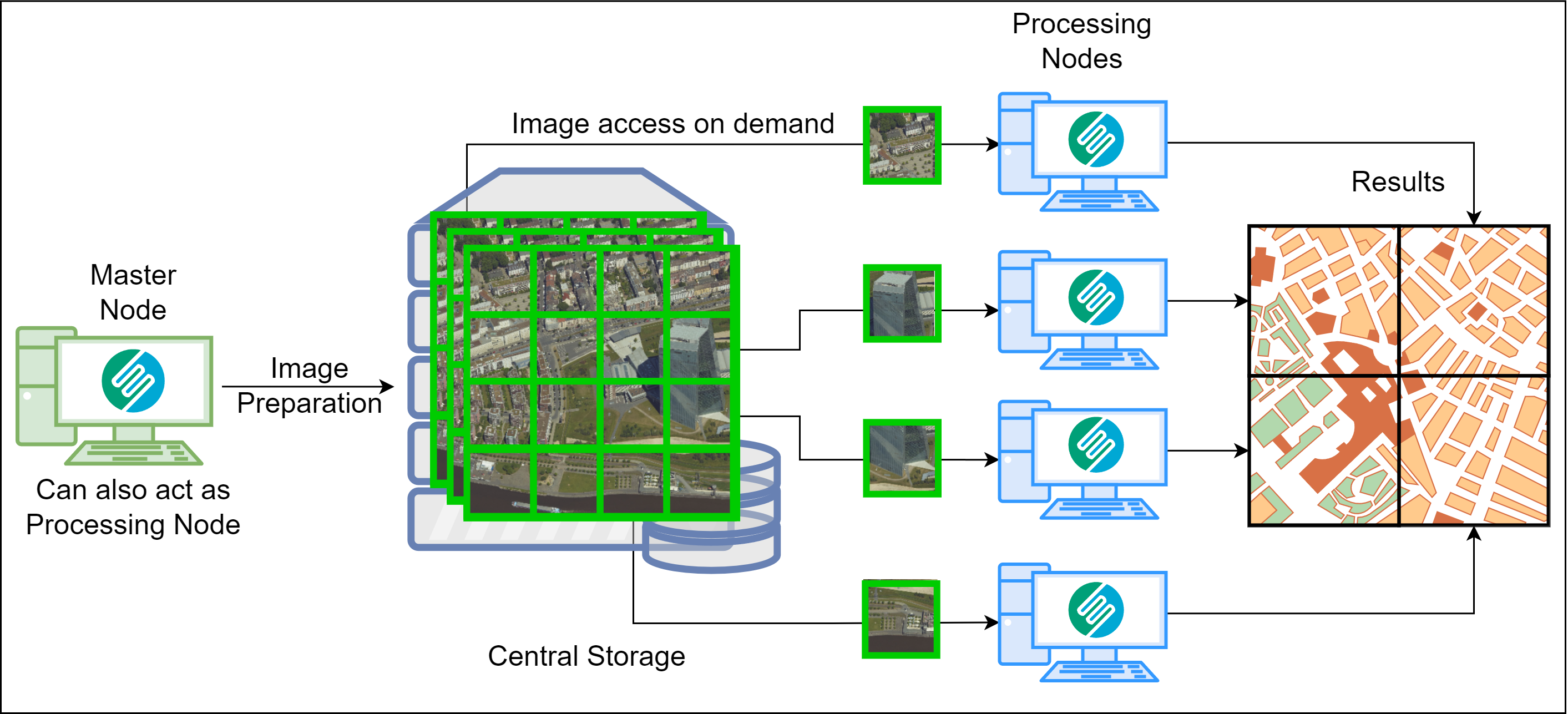
A distributed processing system consists of a cluster of several processing ‘Nodes' that can communicate with each other and coordinate computing tasks.
In SURE, Distributed Processing (DP) is based on a hierarchical structure where one ‘Master' node communicates with 'Processing Nodes' in different machines within the cluster and assigns them tasks.
The Master prepares the Input Images into a central storage location, referred to as Network Image Directory. All Processing Nodes can access this directory, from which they can pull Imagery data, as they are needed.
SURE Distributed Processing divides large projects into smaller sub-projects and distributes them to the processing machines available.
It is worth noting that one can also benefit from DP using a single machine that houses the Master Node and a Processing Node (referred to as Local-DP).
Benefits of Distributed Processing
Easily scale-up production by adding Processing nodes on demand.
Inspect initial results and perform quality assessment within 1 or 2 days.
Minimize progress loss in case of machine restart, power outage, or network disruptions.
Reduce required disk space.
SURE Distributed Processing Workflow
First
The Master:
Prepares Images in the Network Image Directory.
Performs the Analysis step and divides the Project into smaller sub-projects.
Assigns and sends the sub-projects to Processing Nodes.
Then
The Processing Nodes:
Receive sub-project from Master.
Pull and cache Imagery data from the Network Image Directory, as they are needed.
Process sub-project and return results to Master.
Lastly
Once all sub-projects are completed:
The Master merges sub-projects and performs final steps (depending on results requested).